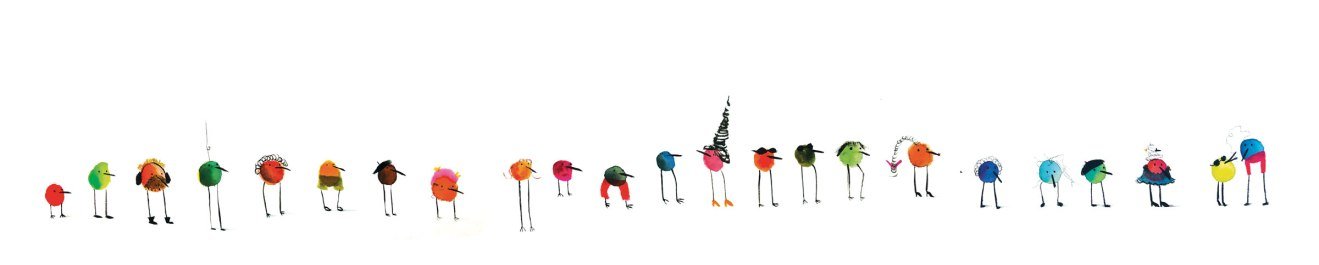We are so excited to have Cindy Derby join us today to share information about writing humorous picture books!
Cindy Derby is an author and illustrator of many critically acclaimed books for children. In 2021 she won a Caldecott Honor for her illustrations in Outside In. The New York Times describes her work as “profound” and “wonderfully out of control.” Cindy lives in San Francisco.
If I sit down at my drawing table and say, "I need to make something funny," I would kill every ounce of my creativity. Instead, I say, "I'm going to make some marks on my paper and see what happens."
It's a relief to work this way. It takes the pressure off of taking myself so seriously. At that moment, I am just a human making a thing. A thing that might be bad. Or it might be alright.
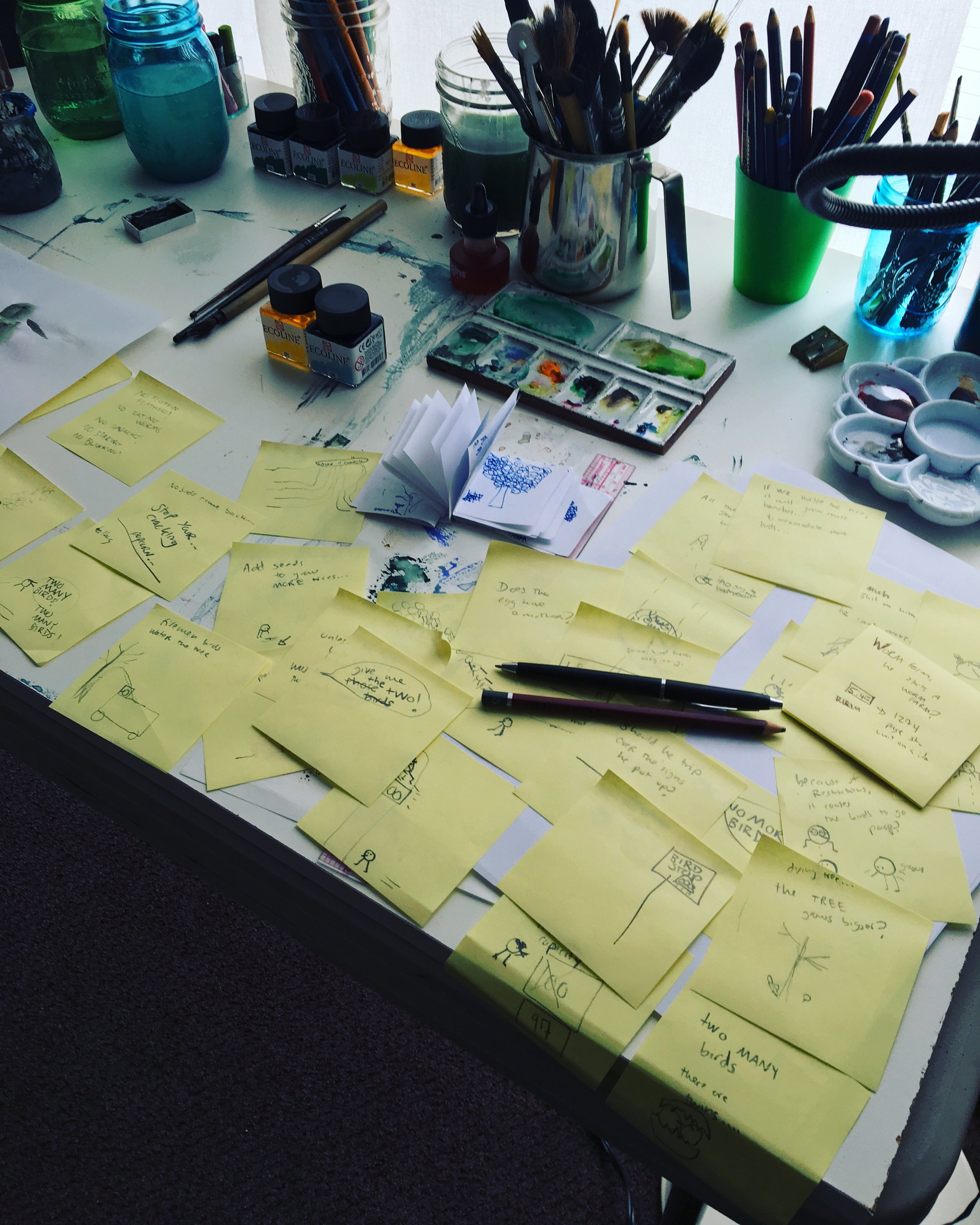
All of my author/illustrated books have originated this way. And sometimes, the mark on the paper turns into a character. And once I decide to hang out with this new character, I take out a massive stack of post-it notes and draw and write anything that pops into my head. I draw it faster than I have time for that critical voice to comment on it—no nice paper for this or expensive pen. The idea isn't ready for that fancy stuff.
When I feel like I am onto something, I put my characters in circumstances that would force various reactions from them.
My upcoming book, Blurp's Book of Manners is a good example of this. I created a character named Ms. Picklepop, with a cupcake style hairdo. She evolved into an etiquette teacher in her fancy mansion. She is inspired by a lady who was the head trainer at a dog academy that my mom and I went to for her two very misbehaved dogs. At the end of the week, the head trainer performed a final dog show on a stage to prove how well-behaved all the dogs became. In between the tricks, the dogs ran around chaotically and pooped everywhere. The trainer covered it up with a smile and pretended it wasn't happening.
After creating Ms. Picklepop for my book, I asked myself what would be the absolute worst thing for this character. And that was easy: a messy paint blob who burps up paint, of course. Taking these two drastically different characters and putting them in a scene together made for some highly amusing moments. I knew I was onto something because it was making me laugh. And that kind of laugh where you are NOT supposed to laugh...because it would be highly inappropriate. Those are the best kinds.
How to Walk an Ant, my debut book, also plays with extremes. A professional ant walker, Amariyah, wants to teach how to walk an ant, but things get a little chaotic when a colony of ants wants to join.
This book is inspired by a drawing I made of a character holding a jump rope. But the jump rope morphed into a leash with ants because I didn't know how to draw a jump rope.
It was so fitting for this character. So out came the massive stack of post-it notes, and the questions. Rules began to emerge and tips on how to successfully walk an ant. Suddenly I was writing out a Nine-Step guide in the voice of this character.
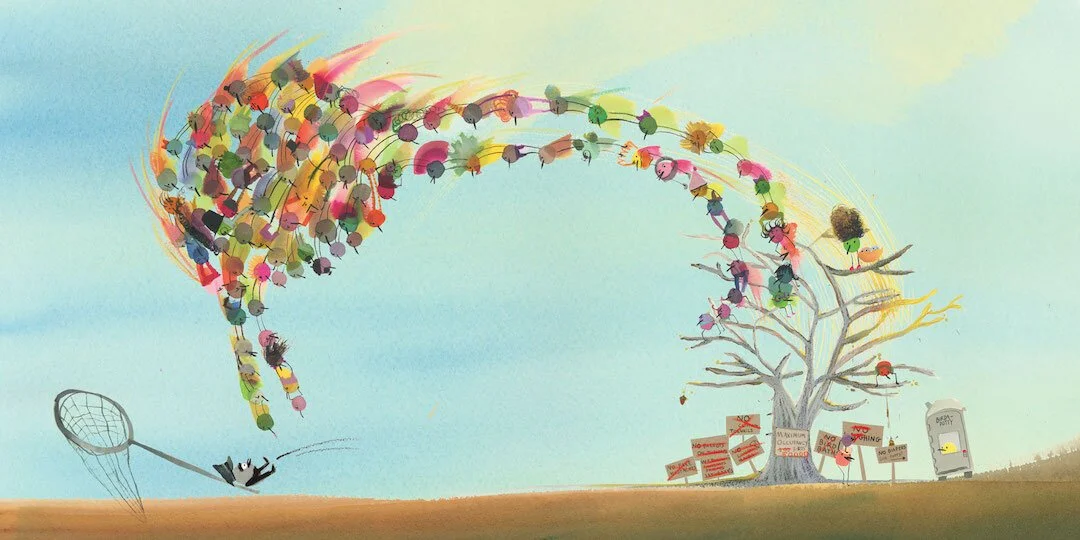
My second author/illustrated book, Two Many Birds, was inspired by a drawing of a very long line of birds.
I asked myself, "what are they waiting for?" And "where does this line lead to?"
Then in my post-it note pile, an idea emerged that they were in line to sit on a tree, which prompted more questions. What if there is a maximum capacity to sit on the tree? And who enforces the rules for this?
These questions prompted my addition of the Bird Monitor, who shouts ridiculous rules. And of course, I asked, "What is the absolute worst thing that could happen to this character?"
Well, if there were too many birds on the tree and if the birds fight back.
I am beginning to see a theme emerge in all of my author/illustrated books— this idea of control versus chaos. I think it is because playing with these extremes makes for some ridiculously absurd scenarios.
Here are a few things I've learned:
Let the character take the lead. Follow them. See where they go.
Don't go into a book saying, "I am going to make a funny book." Instead, start by saying, "Let's see where this goes."
Put this character in a room with someone/something that is the exact opposite of them and see what happens.
Play with extremes. Up the stakes. More. And keep going. You can always dial it down later.
As you go about your daily life, bring around a tiny notebook, or use the Notes app on your phone to jot down funny things that happen or ideas that flash into your head. Otherwise, you will never remember them later.